Business Intelligence Data Warehouse Definition
 Effective decision-making processes in business are dependent upon high-quality information. That's a fact in today's competitive business environment that requires agile access to a data storage warehouse, organized in a manner that will improve business performance, deliver fast, accurate, and relevant data insights. BI architecture has emerged to meet those requirements, with data warehousing as the backbone of these processes.
Effective decision-making processes in business are dependent upon high-quality information. That's a fact in today's competitive business environment that requires agile access to a data storage warehouse, organized in a manner that will improve business performance, deliver fast, accurate, and relevant data insights. BI architecture has emerged to meet those requirements, with data warehousing as the backbone of these processes.
In this post, we will explain the definition, connection, and differences between data warehousing and business intelligence, provide a BI architecture diagram that will visually explain the correlation of these terms, and the framework on which they operate. But first, let's start with basic definitions.
What Is BI Architecture?
Business intelligence architecture is a term used to describe standards and policies for organizing data with the help of computer-based techniques and technologies that create business intelligence systems used for online data visualization, reporting, and analysis.
One of the BI architecture components is data warehousing. Organizing, storing, cleaning, and extraction of the data must be carried by a central repository system, namely data warehouse, that is considered as the fundamental component of business intelligence. But how exactly are they connected?
What Is Data Warehousing And Business Intelligence?
Data warehousing and business intelligence are terms used to describe the process of storing all the company's data in internal or external databases from various sources with the focus on analysis, and generating actionable insights through online BI tools.
One without the other wouldn't function, and we will now explain premises that surround their framework by using a BI architecture diagram to fully understand how data warehouse enhances the BI processes.
BI Architecture Framework In Modern Business
There are various components and layers that business intelligence architecture consists of. Each of that component has its own purpose that we will discuss in more detail while concentrating on data warehousing. But first, let's first see what exactly these components are made of.
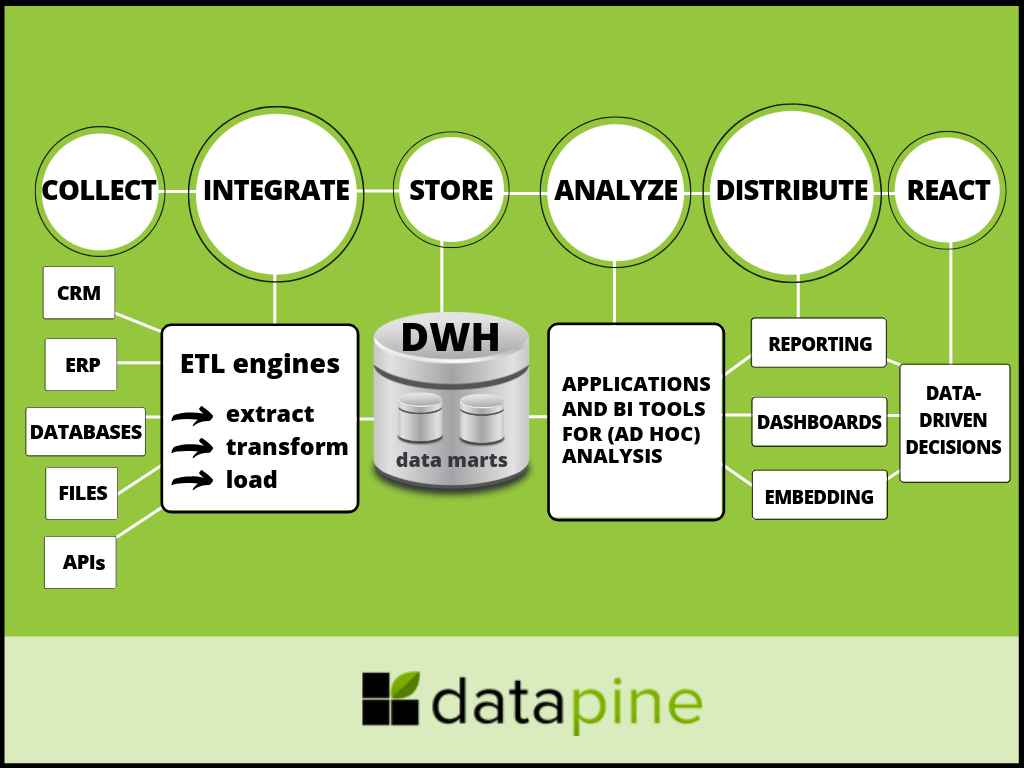
A solid BI architecture framework consists of:
- Collection of data
- Data integration
- Storage of data
- Data analysis
- Distribution of data
- Reaction based on insights
 **click to enlarge**
**click to enlarge**
We can see in our BI architecture diagram how the process flows through various layers, and now we will focus on each.
1. Collection of data
The first step in creating a stable architecture starts in gathering data from various data sources such as CRM, ERP, databases, files or APIs, depending on the requirements and resources of a company. Modern BI tools offer a lot of different, fast and easy data connectors to make this process smooth and easy by using smart ETL engines in the background. They enable communication between scattered departments and systems that would otherwise stay disparate. From a business point of view, this is a crucial element in creating a successful data-driven decision culture that can eliminate errors, increase productivity, and streamline operations. You have to collect data in order to be able to manipulate with it.
2. Data integration
When data is collected through scattered systems, the next step continues in extracting data and loading it to a data warehouse. This process is called ETL (Extract-Transform-Load).
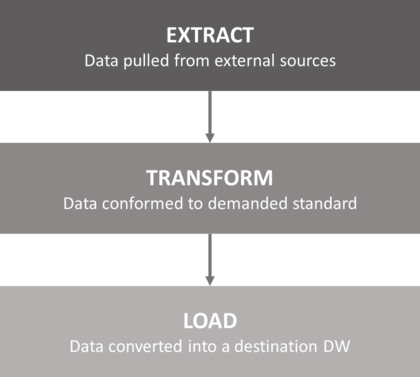
With an increasing amount of data generated today and the overload on IT departments and professionals, ETL as a service comes as a natural answer to solve complex data requests in various industries. The process is simple; data is pulled from external sources (from our step 1) while ensuring that these sources aren't negatively impacted with the performance or other issues. Secondly, data is conformed to the demanded standard. In other words, this (transform) step ensures data is clean and prepared to the final stage: loading into a data warehouse.
3. Data storage
Now we approach the data warehousing and business intelligence concepts. While both terms are often used interchangeably, there are certain differences that we will focus on to get a more clear picture on this topic.
**click to enlarge**
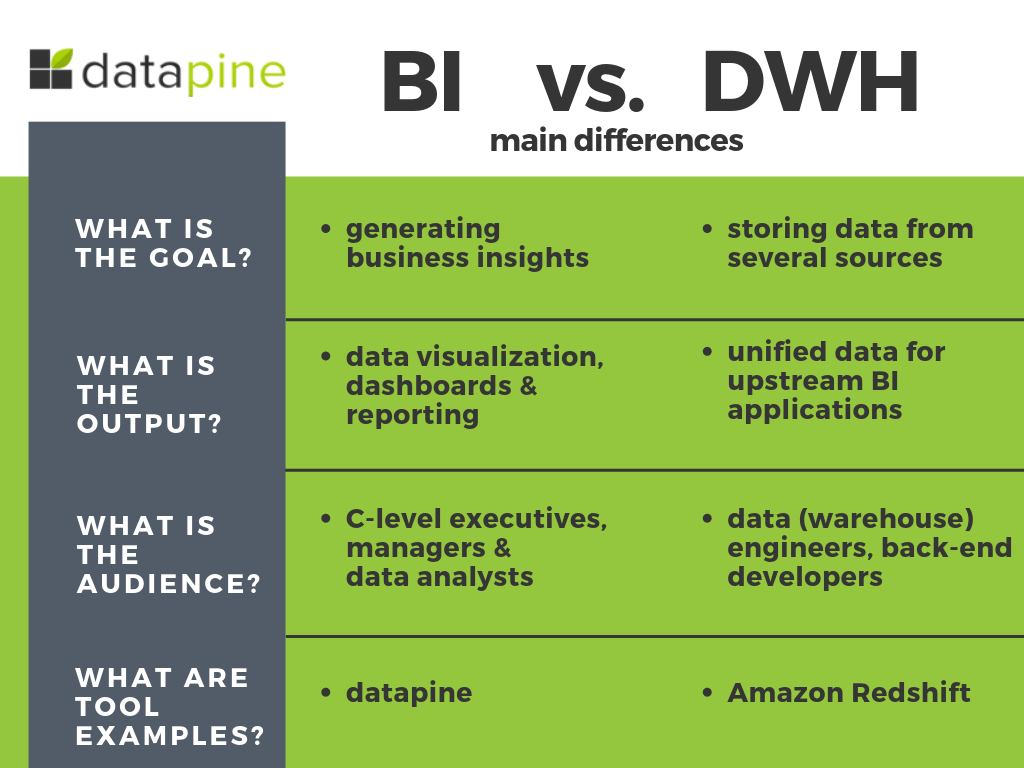
The main differences, as we can also see in the visual, between business intelligence and data warehousing are indicated in these main questions:
a) What is the goal?
Business intelligence and data warehousing have different goals. While they are connected and cannot function without each other, as mentioned earlier, BI is mainly focused on generating business insights, whether operational or strategic efficiency such as product positioning and pricing to goals, profitability, sales performance, forecasting, strategic directions, and priorities on a broader level. The point is to access, explore, and analyze measurable aspects of a business. On the other hand, a data warehouse (DWH) has its significance in storing all the company's data (from one or several sources) in a single place. In a nutshell, BI systems and tools make use of data warehouse while data warehouse acts as a foundation for business intelligence.
b) What is the output?
The output data of both terms also vary. While BI outputs information through data visualization, online dashboards, and reporting, the data warehouse outlines data in dimension and fact tables for upstream applications (or BI tools). Data cleansing, metadata management, data distribution, storage management, recovery, and backup planning are processes conducted in a data warehouse while BI makes use of tools that focus on statistics, visualization, and data mining, including self service business intelligence.
The output difference is closely interlaced with the people that can work with either BI or data warehouse. But let's see this through our next major aspect.
c) What is the audience?
To expand our previous point, the people involved in managing the data are quite different. C-level executives or managers use modern BI tools in the form of a real-time dashboard since they need to derive factual intelligence, create effective sales reports or forecast strategic development of the department or company. CEOs or sales managers cannot manage data warehouse since it's not their area of expertise; they need a tool that will translate the heavy IT data into insights that an average business user can fully understand. That's where business intelligence creates a solid bridge between DWH and BI. On the other hand, a data warehouse is usually dealt with by data (warehouse) engineers and back-end developers. They are the technical chain in a BI architecture framework that design, develop, and maintain systems for future data analysis and reporting a business might need.
d) What are the tools?
With the expansion of data processed and created in our digital age, the tools and software needed to perform analysis expanded and developed in recent years in ways we could not have imagined. In this context, the need for utilizing a proper tool, a stable business intelligence dashboard and data warehouse increased exponentially. In such environment, the data warehouse processes can be managed with a product such as Amazon Redshift while the full support for BI insights needed to effectively generate and develop sustainable business acumen with tools such as datapine. Visualization of data is the core element that enables managers, professionals, and business users to perform analysis on their own, without the need for heavy IT support or work.
Now that we have expounded what is data warehousing and business intelligence, we continue with our next step: analyzing the BI architecture layers needed for establishing a sustainable business development.
4. Analysis of data
In this step of our compact BI architecture, we will focus on the analysis of data after it's handled, processed, and cleaned in former steps with the help of data warehouse(s). The ubiquitous need for successful analysis for empowering businesses of all sizes to grow and profit is done through BI application tools. Especially when it comes to ad hoc analysis that enables freedom, usability, and flexibility in performing analysis and helping answer critical business questions swiftly and accurately.
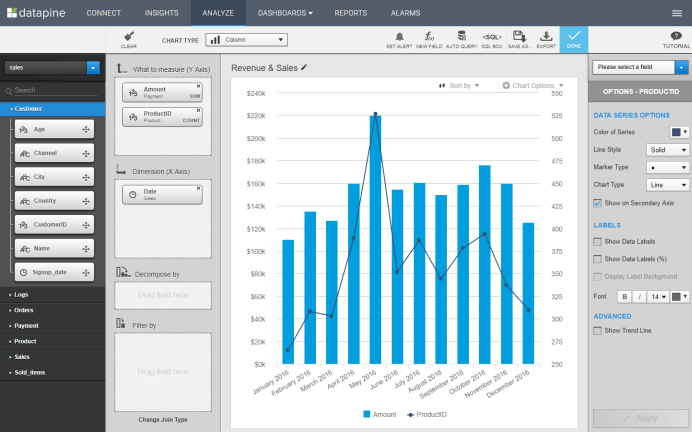
This visual above represents the power of a modern, easy-to-use BI user interface. Modern BI tools like datapine empower business users to create queries via drag and drop, and build stunning data visualizations with a few clicks, even without profound technological knowledge. This simplifies the process of creating business dashboards, or an analytical report, and generate actionable insights needed for improving the operational and strategic efficiency of a business. The data warehouse works behind this process and makes the overall architecture possible.
5. Data distribution
Data distribution comes as one of the most important processes when it comes to sharing information and providing stakeholders with indispensable insights to obtain sustainable business development. Distribution is usually performed in 3 ways:
a) Reporting via automated e-mails: Created reports can be shared with selected recipients on a defined schedule. The dashboards will be automatically updated on a daily, weekly or monthly basis which eliminates manual work and enables up to date information.
b) Dashboarding: Another reporting option is to directly share a dashboard in a secure viewer environment. The users you share with cannot make edits or change the content but can use assigned filters to manipulate data and interact with the dashboard. Another option is to share via public URL that enables users to access the dashboards even if they're outside of your organization, as shown in the picture below:
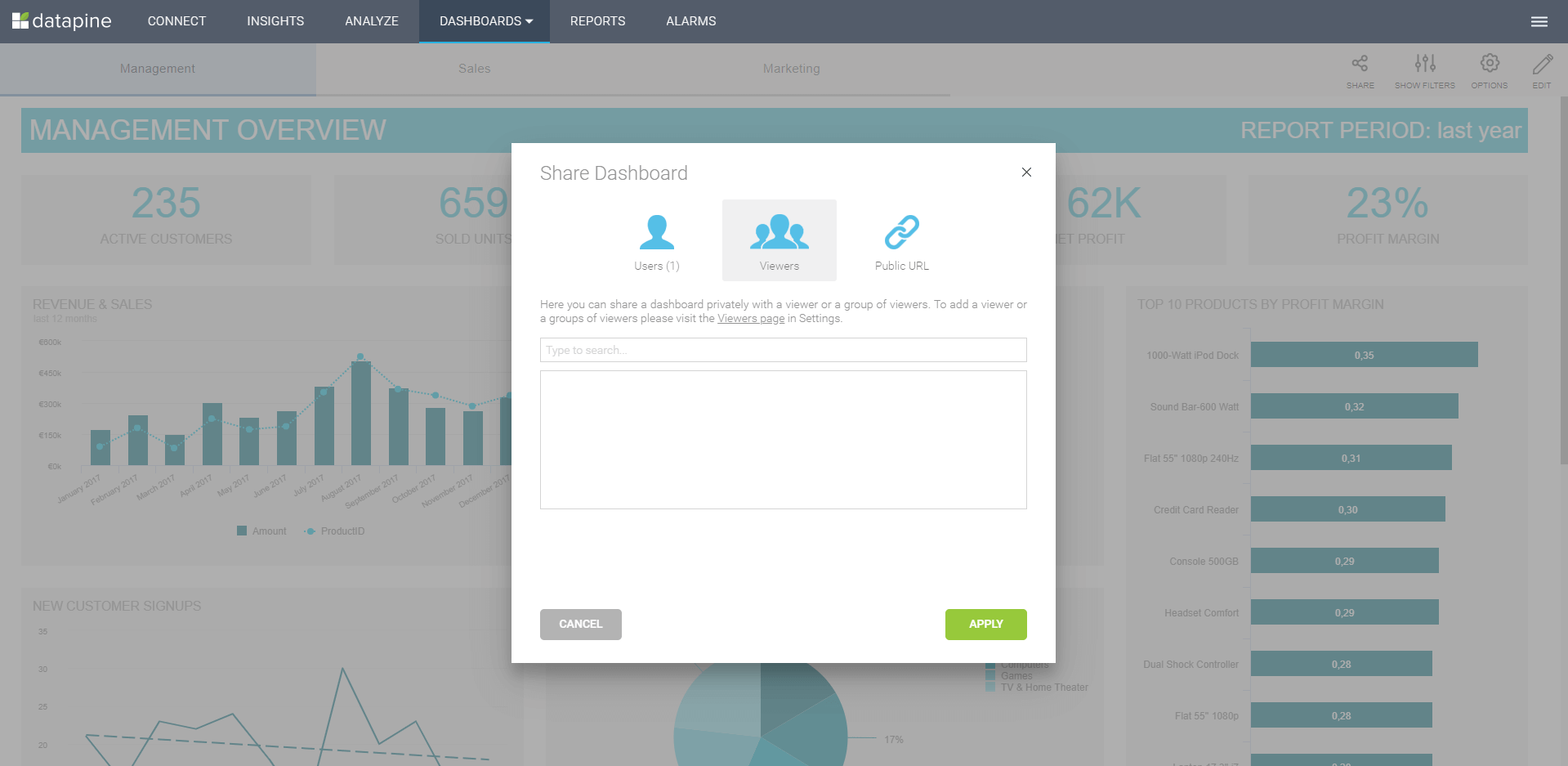
c) Embedding: This form of data distribution is enabled through embedded BI. Your own application can use dashboards as a mean of analytics and reporting without the need for labeling the BI tool in external applications or intranets.
6. Reactions based on generated insights
The final stage where the BI architecture expounds its power is the fundamental part of any business: creating data-driven decisions. Without the backbones of data warehousing and business intelligence, the final stage wouldn't be possible and businesses won't be able to progress. CEOs, managers, professionals, coworkers, and all the interested stakeholders can have the power of data to generate valid, accurate, data-based decisions that will help them move forward. Let's see this through one of our dashboard examples: the management KPI dashboard.
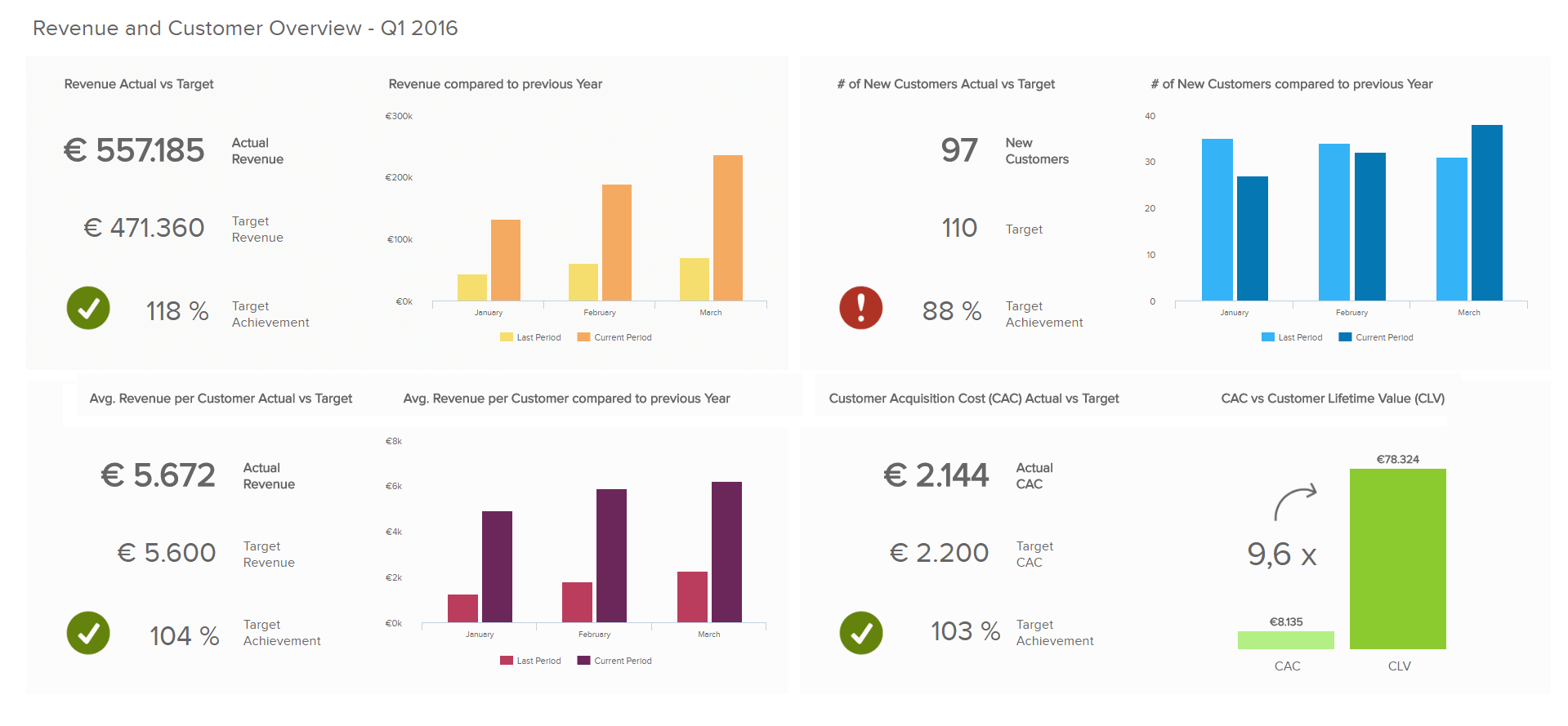
**click to enlarge**
This dashboard is the final product on how data warehouse and business intelligence work together. The processes behind this visualization include the whole architecture which we have described, but it would not be possible to achieve without a firm data warehouse solution. Ultimately, this enables a high-level manager to get a comprehension of the strategic development and potential decisions for creating and maintaining a stable business.
On this particular dashboard, you can see the total revenue, as well as on a customer level, adding also the costs. The targets are also set so that the dashboard immediately calculates if they have been met or additional adjustments are needed from a management point of view. As revenue is one of the most important factors when evaluating if the business is growing, this management dashboard ensures all the essential data is visualized and the user can easily interact with each section, on a continual basis, making the decision processes more cohesive and, ultimately, more profitable.
Data Warehousing And Business Intelligence: Solutions For A Forward-Looking Business
We have explained these terms and how they complement the BI architecture. These processes are important to consider in today's competitive business environment since they bring the best data management practice that can only bring positive results.
Although the terms have been used as synonyms in recent years, today they function on diverse levels, but the perspective is the same: analyze, clean, monitor, and evaluate the data in the finest and most productive way possible.
To use our implemented data warehouse service and modern BI tool, you can sign-up for a 14-day trial, completely free!
Business Intelligence Data Warehouse Definition
Source: https://www.datapine.com/blog/data-warehousing-and-business-intelligence-architecture/#:~:text=What%20Is%20Data%20Warehousing%20And,insights%20through%20online%20BI%20tools.
0 Response to "Business Intelligence Data Warehouse Definition"
Post a Comment